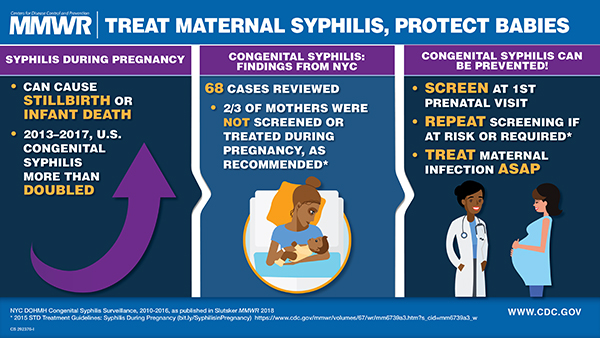
syphilis ,what to know?
syphilis, what to know?
















Recommended approach to the treatment of syphilis. (IM = intramuscular; HIV = human immunodeficiency virus; CSF = cerebrospinal fluid; IV = intravenous)
*--Alternative treatments for nonpregnant penicillin-allergic patients: doxycycline (Vibramycin), 100 mg taken orally twice daily for 2 weeks, or tetracycline, 500 mg taken orally four times daily for 2 weeks; limited data support efficacy for ceftriaxone (Rocephin), 1 g once daily IM or IV for 8 to 10 days, or azithromycin (Zithromax), 2 g orally (single dose).
†--Alternative treatments for nonpregnant penicillin-allergic patients: doxycycline, 100 mg taken orally twice daily for 4 weeks, or tetracycline, 500 mg taken orally four times daily for 4 weeks.
Selected Differential Diagnosis of Genital Lesions
| DISORDER OR DISEASE | CHARACTERISTICS OF GENITAL LESION | ETIOLOGY |
|---|---|---|
Primary syphilis: chancre
|
Solitary, painless ulcer with indurated border
|
Treponema pallidum
|
Secondary syphilis: condyloma latum
|
Slightly raised or flat, round or oval papules covered by gray exudate
|
T. pallidum
|
Genital herpes
|
Cluster of shallow, small, painful ulcers on a red base
|
Herpes simplex virus
|
Chancroid
|
Painful ulcer with sharp, undermined borders
|
Haemophilus ducreyi
|
Venereal warts
|
Soft, usually painless skin-colored or red papules
|
Human papillomavirus
|
Lymphogranuloma venereum: primary stage
|
Painless papule, shallow erosion, or ulcer; may be multiple or single
|
Chlamydia trachomatis
|


Comments
Post a Comment