PRACTICAL QUICK TIPS ON HYPERTENSION TREATMENT
PRACTICAL QUICK TIPS ON HTN TREATMENT
*******************************************
* non-selective || º selective || ^ partial agonist || ª alpha blocker
(x) Average or lowest cost alternative (LCA) price in BC, 1994.
(x) Average or lowest cost alternative (LCA) price in BC, 1994.
* Average or lowest cost alternative (LCA) price in BC, 1994.
source--https://www.ti.ubc.ca/pages/letter8.html
To lower blood pressure in patients with angina pectoris a beta blocker is the drug of first choice. Although we do not have the evidence, it also seems reasonable to use a beta blocker as first choice in patients where the drug can be used to treat more than the hypertension, eg. patients with frequent recurrent migraine or patients with sympathetic hyperactivity, resting tachycardia, and palpitations. Beta blockers should not be used in patients with asthma or other forms of obstructive airways disease.With the evidence presently available, it is advisable when prescribing beta blockers to use a non-selective beta blocker in the lowest dose required to lower the blood pressure
At the present time there are no outcome studies which identify a group of patients who would specifically benefit from a calcium antagonist. It is clear that post MI patients with left ventricular dysfunction do worse with diltiazem than with placebo.(15) An overview of 31 placebo controlled trials submitted to the United States Food and Drug Administration (16) reported that patients receiving calcium antagonists had a 63% excess of cardiac events, as compared to placebo.
From the large controlled studies of the treatment of mild hypertension it is clear that in at least 50% of patients the BP can be controlled with a thiazide alone. The additional drugs used in these studies, for patients not controlled with a thiazide include reserpine in three studies, methyldopa in two studies, hydralazine in two studies, and beta blockers in two studies. We thus can have some confidence in the effectiveness of these drugs used in combination with a thiazide. In patients with moderate to severe hypertension 3 to 4 drugs are often required to adequately control the blood pressure. We, therefore, are fortunate to have a wide armamentarium of drugs to choose from (see Tables).
*******************************************
| Diuretic | Trade Name | Usual Dosage Range | Daily Cost*(in cents) |
| Hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg Chlorthalidone 50 mg | Hydrodiuril®, generic Hygroton®, generic | 12.5 - 25 mg daily 12.5 - 25 mg daily | 0.3 - 0.6 1.2 - 2.4 |
| Bendroflumethiazide 2.5 mg Indapamide 2.5 mg | Naturetin® Lozide® | 1.25 - 2.5 mg daily 2.5 mg daily | 6.6 - 13.3 55.5 |
| Potassium sparing | |||
| HCTZ (25 mg)/triamterene (50 mg) HCTZ (50 mg)/amiloride (5 mg) HCTZ (25 mg)/spironolactone (25 mg) Triamterene (50, 100 mg) Amiloride (5 mg) Spironolactone (25, 100 mg) | Dyazide®, generic Moduret®, generic Aldactazide®, generic Dyrenium® Midamor® Aldactone®, generic | 1/2 - 1 tablet daily 1/4 - 1/2 tablet daily 1/2 - 1 tablet daily 25 - 50 mg daily 2.5 - 5 mg daily 25 - 100 mg daily | 2.5 - 5.0 5.9 - 11.9 5.6 - 11.2 9.9 - 13.1 15.2 - 30.4 8.8 - 27.6 |
Table 2: Beta Blockers
| Beta Blockers | Trade Name | Usual Dosage Range | Daily Cost (x) |
| Propanolol* | Inderal®, generic Inderal® LA | 20-120 mg BID 60-240 mg daily | $0.08-$0.24 $0.47-$1.66 |
| Nadolol* | Corgard®, generic | 20-160 mg daily | $0.15-$0.79 |
| Timolol* | Blocadren®, generic | 5-20 mg BID | $0.36-$1.05 |
| Atenololº | Tenormin®, generic | 25-100 mg daily | $0.20-$0.66 |
| Metoprololº | Betaloc®, Lopressor®, generic Betaloc® SR, Lopressor® SR | 25-100 mg BID 100-200 mg daily | $0.26-$0.48 $0.41-$0.71 |
| Acebutolol^ | Sectral®, Monitan®, generic | 100-400 mg daily | $0.44-$1.32 |
| Oxprenolol^ | Trasicor® Slow Trasicor® | 20-160 mg BID 80-320 mg daily | $0.31-$1.65 $0.83-$1.66 |
| Pindolol*^ | Visken®, generic | 5-15 mg BID | $0.52-$1.31 |
| Labetalol*ª | Trandate® | 100-400 mg BID | $0.52-$1.82 |
| ACE Inhibitors | Trade Name | Usual Dosage Range | Daily Cost (x) |
| Quinapril Ramipril Captopril | Accupril® Altace® Capoten®, generic | 5-40 mg daily 1.25-10 mg daily 12.5-50 mg daily | $0.92 all tablets $0.72-$1.01 $0.45-$1.19 |
| Perindopril Benazepril Cilazapril | Coversyl® Lotensin® Inhibace® | 2-8 mg daily 5-40 mg daily 1-10 mg daily | $0.68-$1.28 $0.61-$1.64 $0.65-$1.69 |
| Lisinopril Fosinopril Enalapril | Prinivil®, Zestril Monopril® Vasotec® | 5-40 mg daily 10-40 mg daily 5-40 mg daily | $0.70-$2.10 $0.84-$2.01 $0.82-$2.36 |
| Calcium Antagonists | Trade Name | Usual Dosage Range | Daily Cost (x) |
| Diltiazem | Cardizem®, generic Cardizem SR® Cardizem CD® | 60-120 mg BID, TID 60-180 mg BID 120-300 mg daily | $0.77-$2.32 $1.50-$3.60 $1.35-$2.98 |
| Verapamil | Isoptin®, generic Isoptin SR® Verelan® | 80-160 mg BID, TID 120-240 mg BID 120-480 mg daily | $0.62-$1.85 $2.07-$3.08 $0.88-$2.45 |
| Nifedipine | Adalat®, generic Adalat PA® Adalat XL® | 5-30 mg BID, TID 10-30 mg BID 30-90 mg daily | $0.55-$1.27 $0.99-$2.54 $1.00-$2.56 |
| Felodipine | Plendil®, Renedil® | 2.5-20 mg daily | $0.54-$2.12 |
| Amlodipine | Norvasc® | 5-10 mg daily | $1.33-$1.94 |
| Nicardipine | Cardene® | 20-40 mg TID | $1.85-$3.70 |
| Alpha 1 Blockers | Trade Name | Usual Dosage range | Daily Cost (x) |
| Prazosin | Minipress®, generic | 1-10 mg BID | $0.34-$1.32 |
| Terazosin | Hytrin® | 1-20 mg daily | $0.64-$2.94 |
| Doxazosin | Cardura® | 1-16 mg daily | $0.58-$3.60 |
| Central and Peripheral Sympatholytics | Trade Name | Usual Dosage Range | Daily Cost (x) |
| Reserpine | Serpasil®, generic | 0.0625-0.25 mg daily | <<$0.01 |
| Methyldopa | Aldomet®, generic | 125 mg - 1 g daily | $0.08-$0.50 |
| Clonidine | Catapres®, generic | 0.05-0.3 mg BID | $0.20-$1.06 |
Table 6: Direct Vasodilators
| Direct Vasodilators | Trade Name | Usual Dosage Range | Daily Cost (x) |
| Hydralazine | Apresoline®, generic | 25-100 mg BID | $0.35-$1.08 |
| Minoxidil | Loniten® | 2.5-40 mg daily | $0.34-$2.96 |
source--https://www.ti.ubc.ca/pages/letter8.html
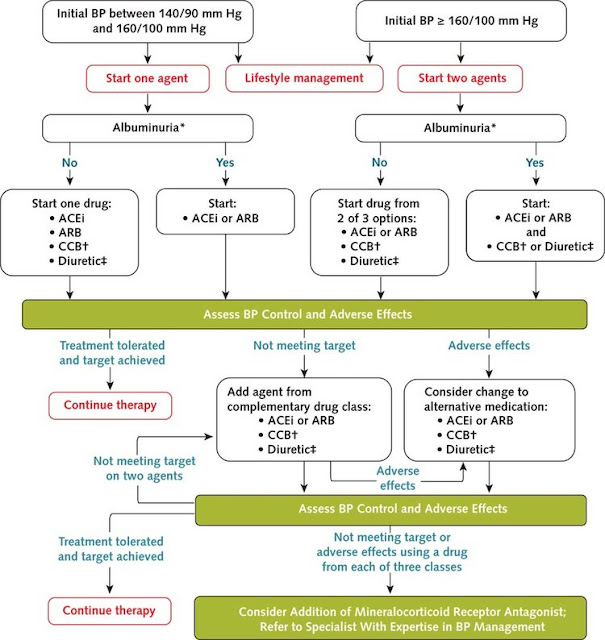
above pics about managing pt DM+HTN
**************************************************************************
**
****
**
***
To lower blood pressure in patients with angina pectoris a beta blocker is the drug of first choice. Although we do not have the evidence, it also seems reasonable to use a beta blocker as first choice in patients where the drug can be used to treat more than the hypertension, eg. patients with frequent recurrent migraine or patients with sympathetic hyperactivity, resting tachycardia, and palpitations. Beta blockers should not be used in patients with asthma or other forms of obstructive airways disease.With the evidence presently available, it is advisable when prescribing beta blockers to use a non-selective beta blocker in the lowest dose required to lower the blood pressure
ACE inhibitors have been clearly shown to prolong survival in patients with congestive heart failure.(12) They are therefore the obvious first choice in patients with hypertension and CHF. It is not established at the present time whether ACE inhibitors have a unique renal protective effect in diabetic nephropathy.(13)
A recent study suggests that ACE inhibitors increase the risk of hypoglycemia in treated diabetic patients.(14) There are no proven therapeutic differences between the ACE inhibitors; drug choice can be made based on convenience and cost. (see Table). The cost can be minimized by prescribing 1/4 or 1/2 tablets whenever possible. (e.g.1/4 of a 20 or 40 mg tablet of quinapril costs $0.23 a day).At the present time there are no outcome studies which identify a group of patients who would specifically benefit from a calcium antagonist. It is clear that post MI patients with left ventricular dysfunction do worse with diltiazem than with placebo.(15) An overview of 31 placebo controlled trials submitted to the United States Food and Drug Administration (16) reported that patients receiving calcium antagonists had a 63% excess of cardiac events, as compared to placebo.
From the large controlled studies of the treatment of mild hypertension it is clear that in at least 50% of patients the BP can be controlled with a thiazide alone. The additional drugs used in these studies, for patients not controlled with a thiazide include reserpine in three studies, methyldopa in two studies, hydralazine in two studies, and beta blockers in two studies. We thus can have some confidence in the effectiveness of these drugs used in combination with a thiazide. In patients with moderate to severe hypertension 3 to 4 drugs are often required to adequately control the blood pressure. We, therefore, are fortunate to have a wide armamentarium of drugs to choose from (see Tables).













Comments
Post a Comment